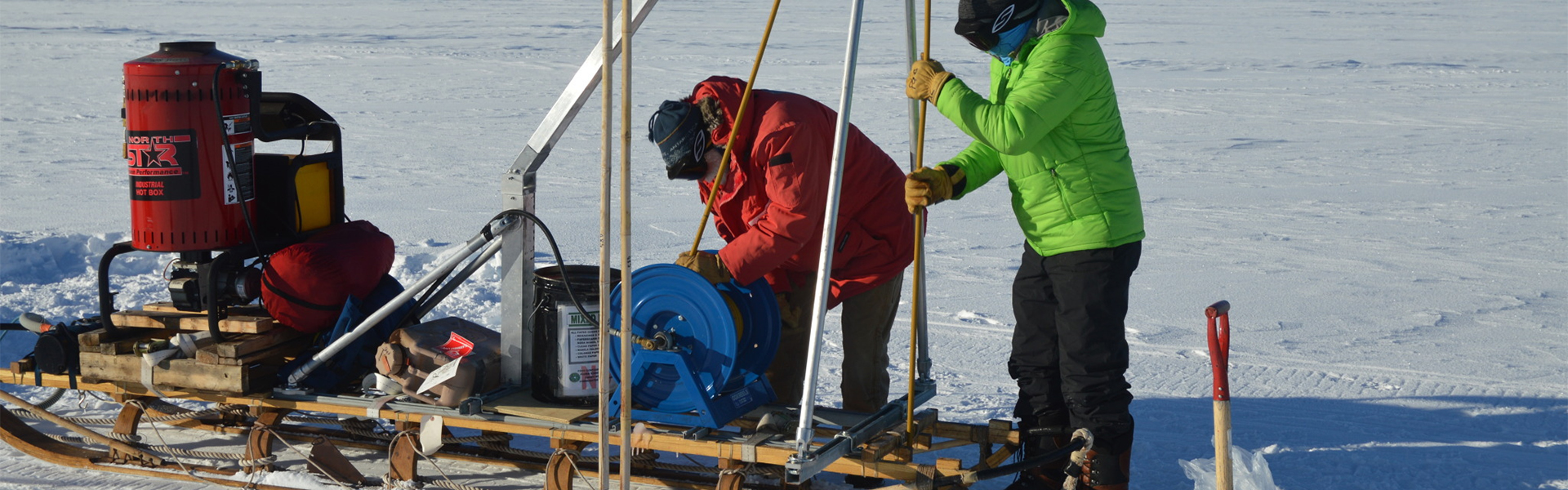
Read the latest news about research conducted by investigators in the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences. Our faculty and students are continually advancing technology, creating solutions and expanding knowledge with new and innovative research.
News
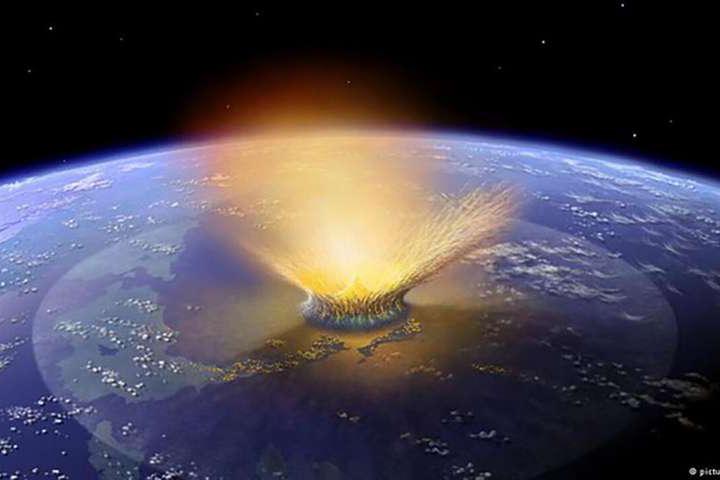
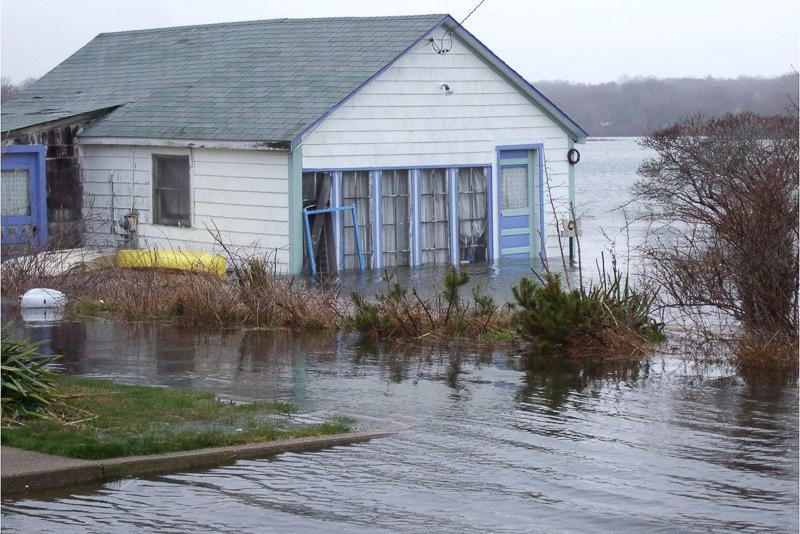
An asteroid impact 66 million years ago may have released trillions of pounds of partially burned fossil carbon into Earth’s upper atmosphere as a cloud of black soot, significantly contributing to the ensuing global darkness, cooling and mass extinction that wiped out the dinosaurs, according to an international team of scientists.
Even though State governments routinely rely upon interest groups to help them as they craft legislation, researchers found that certain peer-leader states, like Pennsylvania and Colorado, have greater influence in shaping states’ fracking policies, in a study led by Penn State Professor of Geography Jennifer Baka.
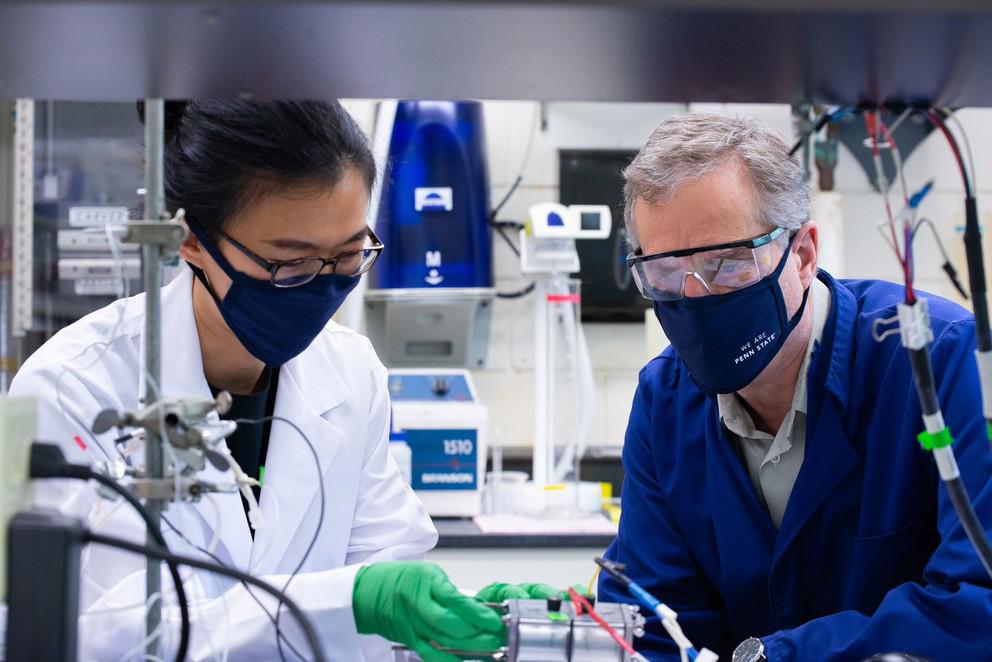
The power of the sun, wind and sea may soon combine to produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel, according to a team of Penn State researchers.
As the globe warms, the atmosphere is becoming more unstable, but the oceans are becoming more stable, according to an international team of climate scientists, who say that the increase in stability is greater than predicted and a stable ocean will absorb less carbon and be less productive.
Typically, computer models of climate become more and more complex as researchers strive to capture more details of our Earth's system, but according to a team of Penn State researchers, to assess risks, less complex models, with their ability to better sample uncertainties, may be a better choice.
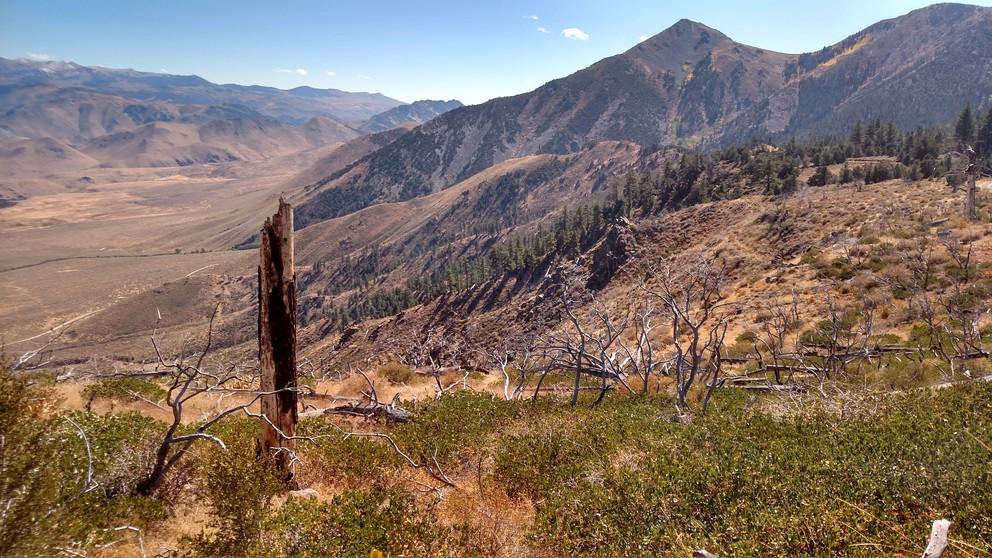
A warming climate and more frequent wildfires do not necessarily mean the western United States will see the forest loss that many scientists expect.
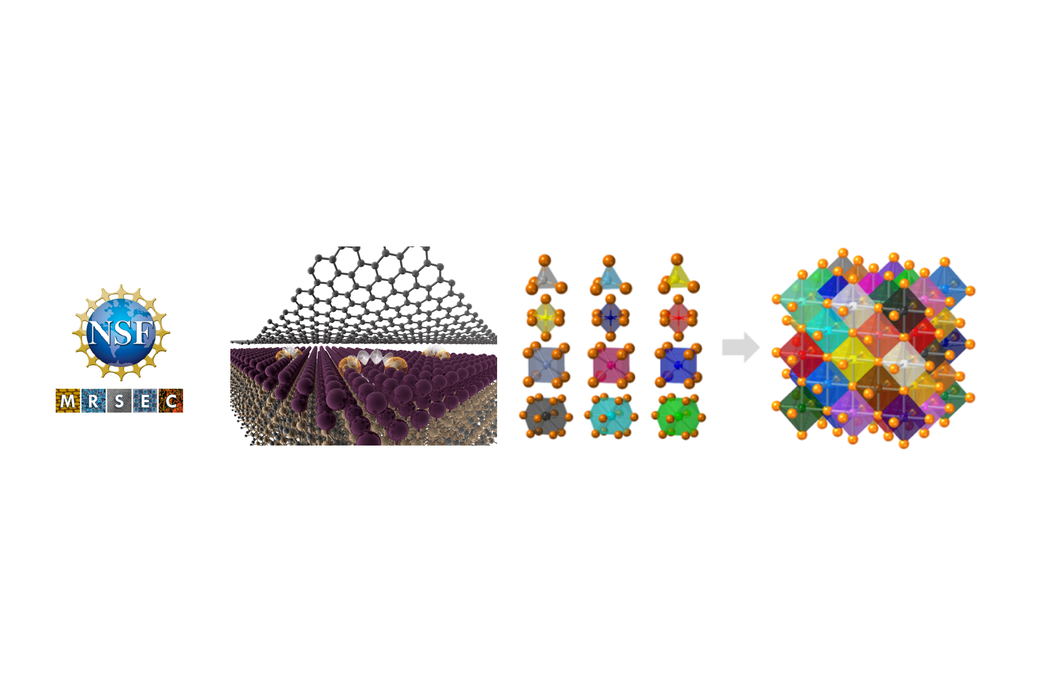
The Center for Nanoscale Science, a National Science Foundation Materials Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC), has again successfully renewed its NSF support in the highly competitive MRSEC program. The new iteration of the center encompasses two of NSF’s Big Ideas — "Quantum Leap" and "Harnessing the Data Revolution."
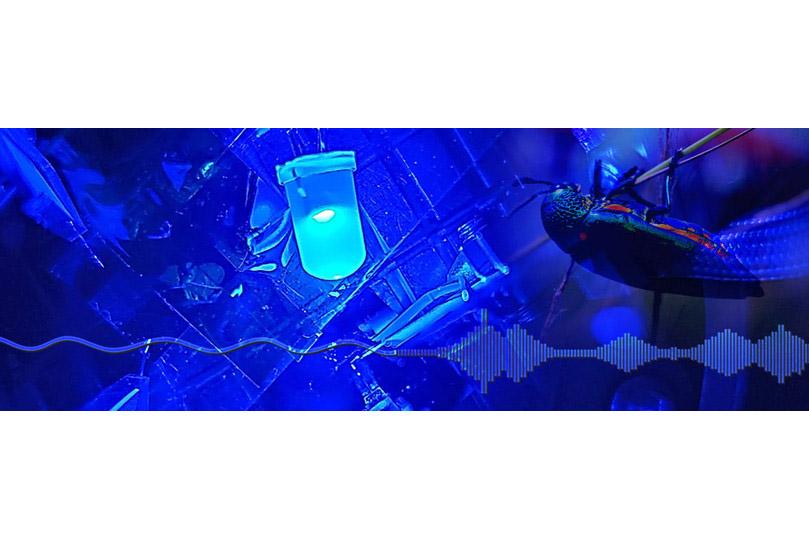
Adding noise to enhance a weak signal is a sensing phenomenon common in the animal world but unusual in manmade sensors. Now Penn State researchers have added a small amount of background noise to enhance very weak signals in a light source too dim to sense.
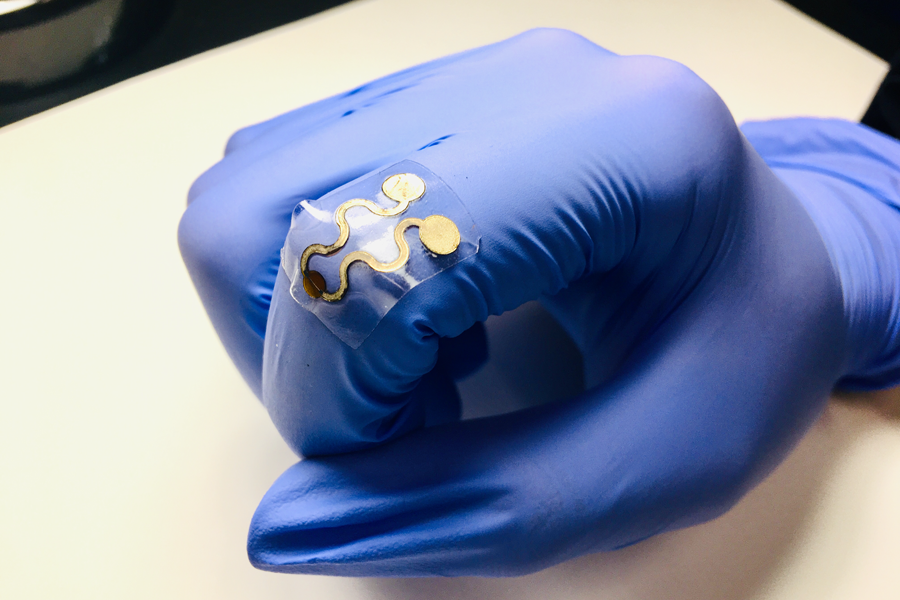
A stretchable, wearable gas sensor for environmental sensing has been developed and tested by researchers at Penn State, Northeastern University and five universities in China.
Plant-based biofuels can play a key role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and removing excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and growing these crops in certain landscapes offers net climate benefits compared to other land use options, according to a team of international scientists.